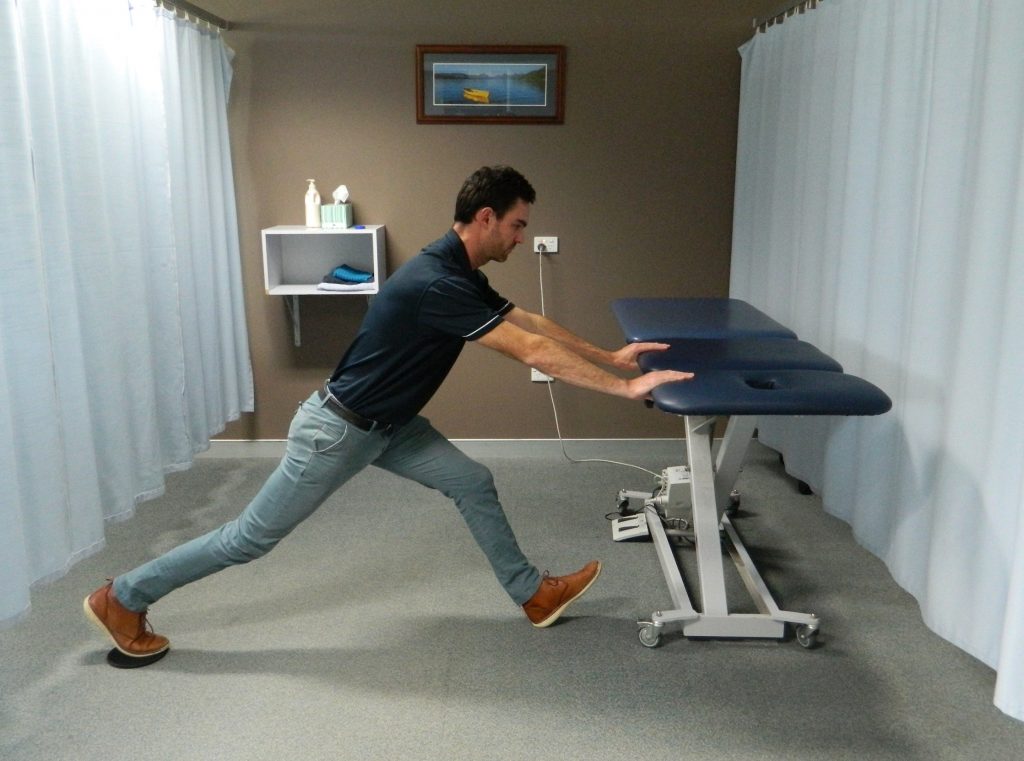
Athletes rejoice! For decades our understanding of hamstring (HS) injuries has been improving and evolving, yet the frequency of HS injury rates in sport have not declined. Finally, a new paradigm has been developed which consolidates our knowledge of the anatomy and the physiology of this highly prevalent injury, applies effective rehabilitation strategies, accurate return to sport testing and re-injury prevention.
We can broadly define the typical hamstring strain into a sprinting type strain which occurs at high speed running versus a stretch type strain which occurs with high kicking or other stretching movements. Each of these will typically cause an injury to a different muscle in the hamstrings group. They can generally be diagnosed in the clinic without the need for any imaging. The most common type is the sprinting type, frequently seen in football codes, soccer, hockey, athletics and other running sports. The stretch type is more common in dancers, jumpers and hurdlers, although either type can occur in any sport. Knowing the type of injury gives us a chance to apply the right exercise rehab as well as gives a guideline for the return to sport time, which varies enormously between the type, location and grade of strain.
We know that most HS injuries occur when the muscle is working hard in its lengthening phase, therefore it is essential that the rehabilitation program targets this movement at high load. A comprehensive program is undertaken, which incorporates hamstring strength, but also hip, pelvis, trunk and general lower limb strength and stability. This addresses all the factors which will lead to re-injury – that’s not new. What is new is a set of 3 specific exercises, that when applied correctly in soccer players led to a re-injury rate of only 1 in 75 players over 12 months! That’s way down from the average 1 in 4 players with conventional rehab in professional soccer.
The protocol is based on 3 specific lengthening (eccentric) strength exercises and the technique, timing and progressions of these are of critical importance, they need to be integrated and complemented with other exercises and, as a rule, should be pain free. So what can you expect to gain from completing a modern rehab program like the one we provide at NU Moves? A research study by Askling and colleagues found that their protocol of exercises led to an average return to play time of 28 days, compared with 51 days for the conventional group. Combining this with the low reinjury rate means it was proven to be a much better approach to HS rehab. The research also provided an additional return to play testing procedure (H test), which we integrate into our comprehensive existing return to play algorithm in the clinic. It assesses apprehension or feeling of insecurity as well as pain when performing a high load eccentric braking action on the leg, similar to what happens during an injury but in a safe way.
So to put it all together, we have a rehab protocol that fits well with our current understanding of hamstring strains and their risk factors. It is easy and inexpensive to perform once taught. It also reduces the time to return to play and gives better long-term outcomes. If you are ever unlucky enough to be in this position, then things are looking better now than they ever have!
NU Moves physio provides sports physio services to clubs around newcastle. For more information contact us online or give us a call and to view our current sports teams or what services we provide, click here.













 The NU Moves Physio team has recently completed a masterclass debating the best approach to manage and treat adductor pain and tendon problems with footballers. Journal articles were found and discussed relative to the NU Moves approach to diagnosis and treatment.
The NU Moves Physio team has recently completed a masterclass debating the best approach to manage and treat adductor pain and tendon problems with footballers. Journal articles were found and discussed relative to the NU Moves approach to diagnosis and treatment.